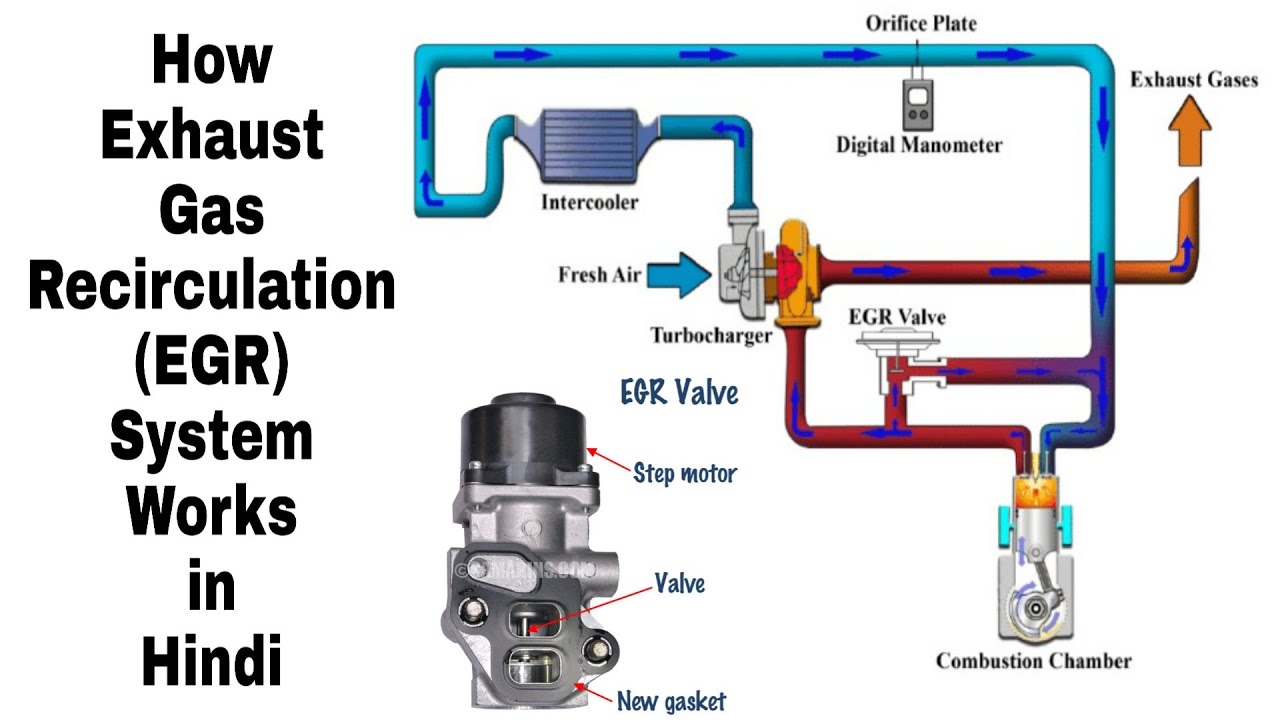
What is EGR? EGR stands for Exhaust Gas Recirculation, a critical technology used in modern internal combustion engines to reduce emissions and improve overall efficiency. EGR systems work by recirculating a portion of the engine's exhaust back into the intake manifold, which helps lower combustion temperatures and, as a result, reduces the formation of nitrogen oxides (NOx), a harmful pollutant. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of EGR, how it functions, its benefits, and its impact on engine performance.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, understanding technologies like EGR is essential for both manufacturers and consumers. With the automotive industry shifting towards greener alternatives, EGR plays a vital role in helping meet these standards without sacrificing performance. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of EGR, its workings, and its relevance in today's automotive landscape.
We will delve deeper into the various types of EGR systems, their advantages and disadvantages, and how they affect engine health and maintenance. Whether you're a car enthusiast, a mechanic, or simply someone looking to understand more about your vehicle, this guide will equip you with valuable knowledge about EGR and its significance.
Table of Contents
- What is EGR?
- How EGR Works
- Types of EGR Systems
- Benefits of EGR
- Disadvantages of EGR
- EGR and Engine Performance
- EGR Maintenance
- The Future of EGR Systems
What is EGR?
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) is a crucial emission control technology that has been a part of internal combustion engines for several decades. By recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the engine's intake system, EGR helps in lowering the peak combustion temperatures. This reduction in temperature is significant because high temperatures lead to the formation of harmful nitrogen oxides (NOx), which are a major contributor to air pollution.
In essence, EGR contributes to cleaner exhaust emissions while simultaneously improving the engine's efficiency. It is particularly important in diesel engines, which tend to produce higher levels of NOx compared to gasoline engines. As manufacturers strive to meet stringent emission regulations, EGR has become a standard component in many vehicles today.
How EGR Works
The EGR system consists of several key components, including an EGR valve, a control module, and a network of pipes connecting the exhaust and intake systems. Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how EGR works:
- Exhaust Gas Collection: During the engine's operation, a portion of the exhaust gases is directed towards the EGR valve.
- Flow Control: The EGR valve opens and closes based on engine load, temperature, and other parameters. This control is typically managed by the engine control unit (ECU).
- Recirculation: Once the valve is open, the exhaust gases flow back into the intake manifold, mixing with the incoming air-fuel mixture.
- Combustion: The mixture of fresh air and recirculated exhaust gases is then compressed and ignited in the combustion chamber.
Types of EGR Systems
There are primarily two types of EGR systems used in modern vehicles:
1. Positive Pressure EGR
In positive pressure EGR systems, exhaust gases are introduced into the intake manifold under pressure. This type of system is more common in diesel engines, where exhaust gases are forced back into the intake stream through a complex network of piping.
2. Negative Pressure EGR
Negative pressure EGR systems utilize the vacuum created by the intake manifold to draw exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber. This type is more commonly found in gasoline engines. The EGR valve opens when the engine is under load, allowing exhaust gases to mix with fresh air.
Benefits of EGR
Implementing an EGR system in modern engines offers several benefits, including:
- Reduced Emissions: EGR significantly lowers NOx emissions, helping vehicles comply with environmental regulations.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: By optimizing combustion temperatures, EGR can enhance fuel efficiency and overall engine performance.
- Engine Longevity: Lower combustion temperatures can contribute to reduced engine wear, extending the lifespan of engine components.
Disadvantages of EGR
Despite its advantages, EGR systems also come with certain drawbacks, such as:
- Carbon Buildup: The recirculated exhaust gases can lead to carbon deposits accumulating in the intake manifold and EGR valve, potentially causing blockages.
- Complexity: EGR systems add complexity to the engine design, which can lead to increased maintenance and repair costs.
EGR and Engine Performance
The relationship between EGR and engine performance is a topic of much discussion among automotive professionals. While EGR can help reduce emissions and improve fuel efficiency, it can also impact engine power output. Here are some key points:
- Power Loss: The introduction of exhaust gases can dilute the air-fuel mixture, potentially leading to a decrease in power output.
- Tuning Adjustments: Many performance enthusiasts adjust EGR settings to maximize horsepower while still adhering to emission regulations.
EGR Maintenance
Proper maintenance of the EGR system is essential to ensure its optimal functioning. Regular checks and cleanings can help prevent issues related to carbon buildup. Here are some maintenance tips:
- Perform regular inspections of the EGR valve and related components.
- Clean the intake manifold periodically to remove carbon deposits.
- Replace faulty EGR valves promptly to prevent performance issues.
The Future of EGR Systems
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, EGR systems will likely see advancements in technology and design. With the rise of electric and hybrid vehicles, the role of traditional EGR systems may change, but their importance in reducing emissions in combustion engines will remain significant.
Conclusion
In summary, Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) is a vital technology in modern internal combustion engines, playing a crucial role in reducing emissions and enhancing fuel efficiency. Understanding how EGR works, its benefits, and its challenges can help vehicle owners make informed decisions regarding their maintenance and performance. We encourage you to leave your thoughts in the comments, share this article with others who may find it helpful, and explore more on our website.
Final Thoughts
Thank you for taking the time to read this comprehensive guide on EGR. We hope it has enriched your understanding of this important technology and its implications for automotive performance and environmental responsibility. We look forward to seeing you again on our site for more insightful articles!
ISO Industrial Services Louisiana: Your Comprehensive Guide
Raising Cane's Hours: Everything You Need To Know
Understanding Cheerleader Outfit Malfunction: A Comprehensive Guide